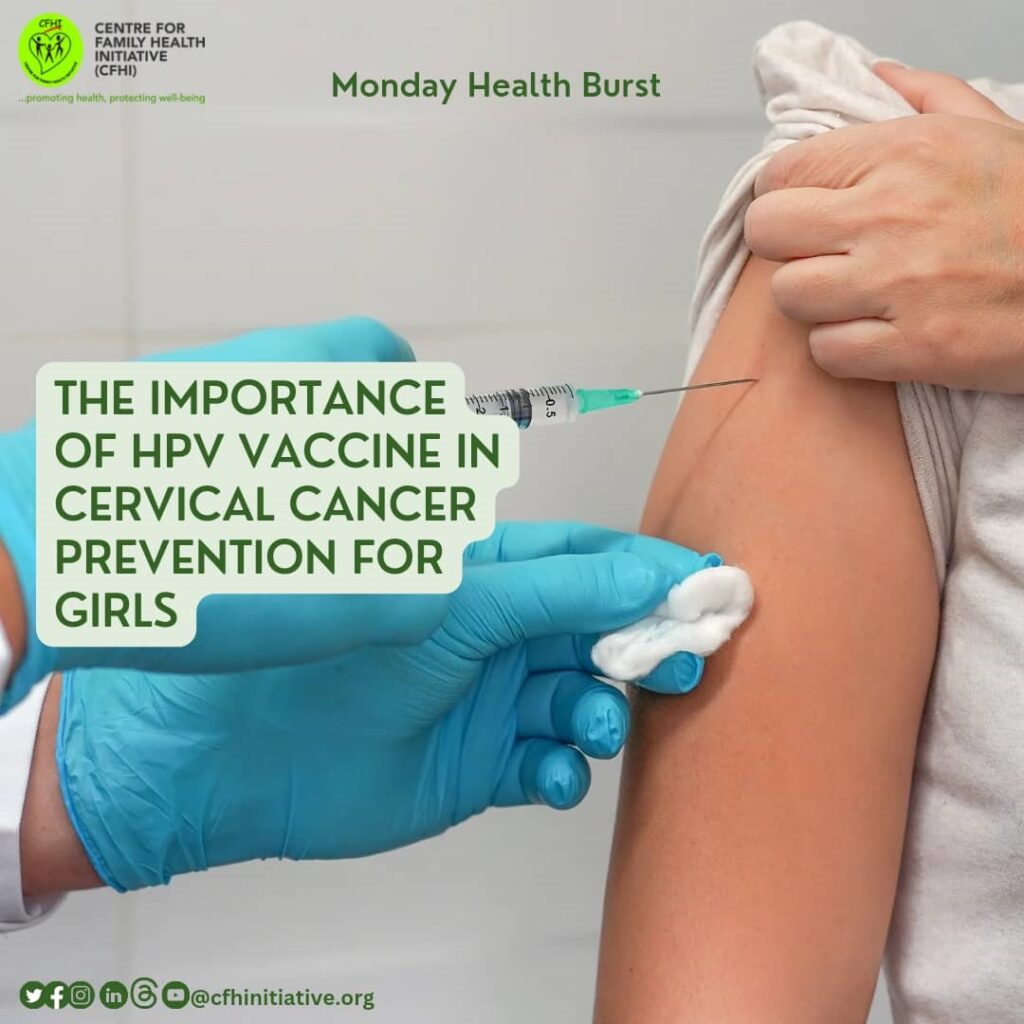
MONDAY HEALTH BURST ON HEART HEALTH IN MEN: REDUCING CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE RISK
The World Health Organization reports that in 2019, an estimated 17.9 million people died from cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), accounting for 32% of all global deaths.1 As a leading cause of death among men worldwide, cardiovascular disease presents significant but often preventable risks. By understanding these risk factors and adopting healthy lifestyle changes, men can take proactive steps to greatly reduce their chances of developing heart-related conditions.
CVD encompasses various conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Men, especially in middle age, face higher risks due to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. As men tend to develop CVD at younger ages than women, early prevention is critical.
Several modifiable risk factors contribute to CVD in men. High blood pressure is a common cause, as it damages arteries and strains the heart. Managing blood pressure through regular monitoring, reducing sodium intake, and managing stress is essential. High LDL (bad) cholesterol, another major risk, can lead to artery blockages. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help maintain cholesterol levels.
Smoking greatly raises heart disease risk by damaging blood vessels and lowering oxygen levels in the blood, making quitting one of the most impactful steps toward a healthier heart. Physical inactivity also increases the risk of heart disease; regular exercise strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and controls weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Diabetes is another risk factor, as high blood sugar can damage blood vessels. Managing diabetes through proper diet, regular exercise, and medication reduces the risk.
Men can improve heart health with a few practical lifestyle changes. Adopting a heart-healthy diet that includes low saturated fats, high fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is crucial, along with incorporating omega-3-rich foods like salmon and walnuts, which promote cardiovascular health. Regular exercise is also essential, as it strengthens the heart and boosts circulation. Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly important, as obesity increases the risk of heart disease and related conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. Even modest weight loss can lead to significant heart health benefits.
Stress management is another key component of heart health. Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure and unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating or smoking. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress.
Finally, routine check-ups allow for early detection and monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. Discussing family history with a healthcare provider is also crucial for assessing overall risk and creating a personalized plan for heart health.
Reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease is within reach through consistent lifestyle changes and preventive care. A heart-healthy diet, active lifestyle, quitting smoking, stress management, and regular health screenings are all effective ways to lower the risk of heart disease. By prioritizing heart health today, men can prevent complications and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
Reference:

MONDAY HEALTH BURST ON HEART HEALTH IN MEN: REDUCING CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE RISK Read More »