SPEAK WEDNESDAY
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION AND ITS EFFECTS
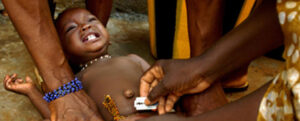 “Have you ever heard of Female genital mutilation? The doctor asked me. This was after my over 20 hours of labor, an ordeal which left me depressed for over a month. It took me a while before I responded because it was the least question I ever would imagine answering at such moment.
“Have you ever heard of Female genital mutilation? The doctor asked me. This was after my over 20 hours of labor, an ordeal which left me depressed for over a month. It took me a while before I responded because it was the least question I ever would imagine answering at such moment.
I had just come out of one of the difficult deliveries he had ever carried out he continued after I replied “yes”. A delivery which at first didn’t seem like I was going to spend more than 6 hours at most because I was 100% effaced and with my labor progression, getting dilated would not be so much of a trouble. After being fully dilated and the baby just wouldn’t come down the delivery canal, an assisted delivery using a vacuum extractor was performed which left me with a vaginal hematoma and still with no baby, I was opted for a caesarean section due to the excessive bleeding and the other effects an obstructed labor has on both mother and unborn child. After all the medical jargons, he finally disclosed I had been genitally mutilated probably as a child and it was the reason for the complications I had just experienced.”
The above near death experience was recounted by Mrs Mary Alex, a human rights activist and a current volunteer at Centre for Family Health Initiative ……….
Female genital mutilation (FGM) is a traditional practice that has no medical benefit and severe health consequences for girls and women. According to Wikipedia, It is a procedure that involves partial or completely removing the external females genitalia or other injury to the female genital organs whenever for non-medical reasons. FGM is recognized internationally as a violation of the human rights of girls and women. It deprives them of the opportunity to make critical and informed decisions about their sexuality. It is an act which is deeply rooted in cultural beliefs and perceptions. Data shows that Nigeria, due to its large population, has the highest number of female genital mutilation (FGM) worldwide. About 20 million women and girls in Nigeria have undergone female genital mutilation which is 10% of the global total.
There are 4 types of FGM; Type I, Type II, Type III and Type IV. Types I and II are most prevalent, but variation exists within countries and communities. Type III is experienced by about 10 per cent of all affected women. FGM has serious implications for the sexual and reproductive health of girls and women. Its effects vary depending on the type performed, the expertise of the practitioner and the conditions under which it is performed. Complications can include severe pain, shock, hemorrhage, infection, urine retention and more. In some cases, hemorrhage and infection can be severe enough to cause death. Long-term risks include complications during childbirth (difficult delivery, excessive bleeding, caesarean section, need to resuscitate the baby, etc.) and newborn deaths; vaginal problems (discharge, itching, bacterial vaginosis and other infections); menstrual problems (painful menstruations, difficulty in passing menstrual blood, etc.); scar tissue and keloid; sexual problems (pain during intercourse, decreased satisfaction, etc.) and psychological problems (depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, low self-esteem, etc.) among others.
Despite the graveness of the issue, the practicing societies consider it as a necessary part of raising a girl, and a way to prepare her for adulthood and marriage. It is seen as a sure medium to ensure premarital virginity and marital fidelity.
Currently, 13 out of 36 states in Nigeria have their own individual state laws expressly prohibiting FGM/C. These states are Lagos, Osun, Ondo, Ekiti, Bayelsa, Ogun, Delta, Ebonyi, Oyo, Imo, Edo, Cross-River and Rivers. The 2015 Violence Against Persons Prohibition Act (VAPP) acknowledges FGM as a criminal act, however since its enactment, there has been no convictions. Out of the 36 states, only 4 states: Abuja, Anambra, Oyo and Ebonyi have domesticated or actively enforced the law.
Speak Wednesday is an initiative of CFHI to address issues of gender based violence and gender inequality. Join us every Wednesday on all our social media platforms for more episodes.

