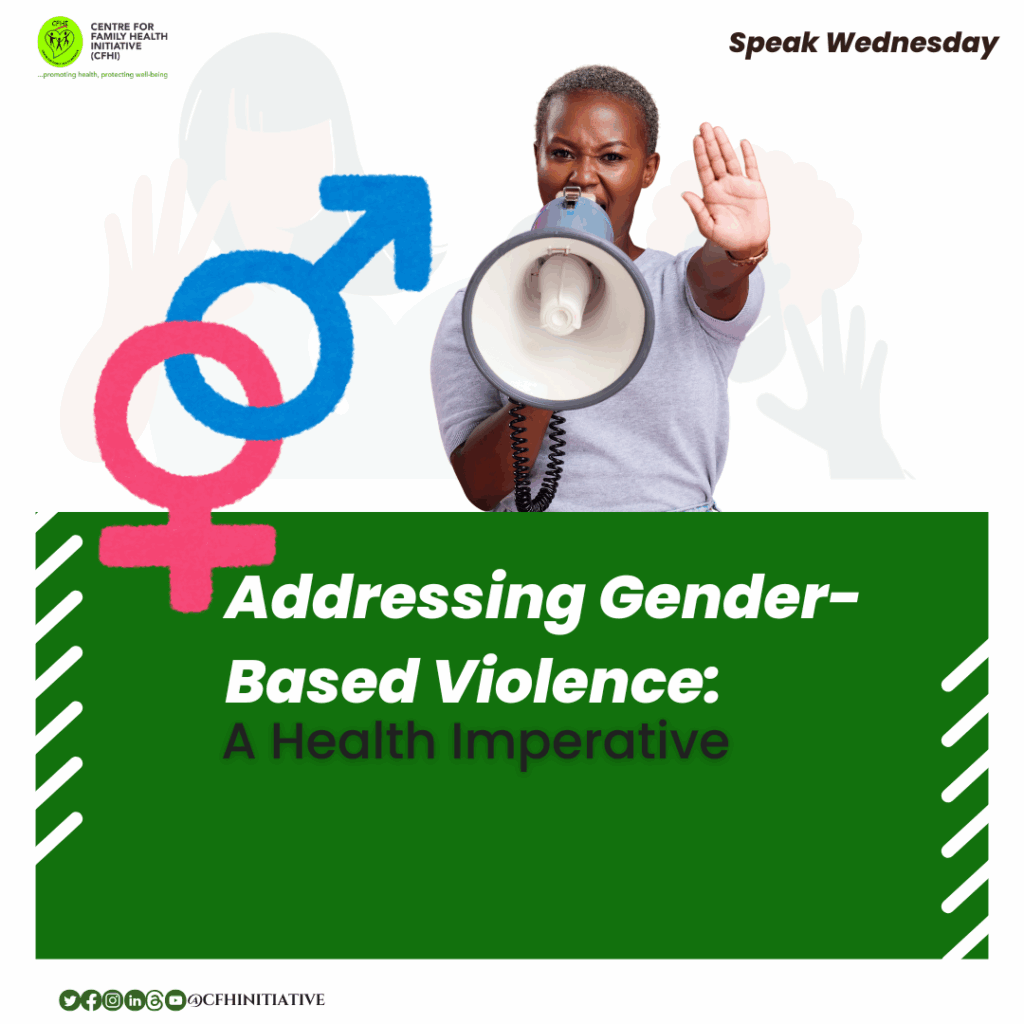
SPEAK WEDNESDAY ON ADDRESSING GENDER-BASED VIOLENCE: A HEALTH IMPERATIVE
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) is not merely a social injustice; it is a profound public health crisis that demands immediate and sustained attention. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly 1 in 3 women worldwide have been subjected to physical and/or sexual violence by an intimate partner or non-partner sexual violence, or both.
The Health Consequences of GBV
The repercussions of GBV extend far beyond immediate physical injuries. Survivors often face long-term health issues, including chronic pain, gastrointestinal disorders, and sexually transmitted infections. Mental health is also severely impacted, with increased risks of depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and suicidal tendencies. WHO emphasizes that GBV has significant and long-lasting impacts on physical and mental health, including injury, unintended pregnancy, pregnancy complications, sexually transmitted infections, HIV, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and even death.
GBV as a Barrier to Gender Equality
GBV perpetuates gender inequalities, hindering women’s and girls’ access to education, economic opportunities, and political participation. It reinforces societal norms that devalue females, creating an environment where discrimination and violence are tolerated.
The Role of the Health Sector
Healthcare providers are often the first point of contact for survivors. Therefore, the health sector plays a crucial role in identifying and supporting victims. This includes providing medical care, psychological support, and referrals to legal and social services. Training healthcare workers to recognize signs of abuse and respond appropriately is essential.
Policy and Legal Frameworks
Furthermore, robust legal frameworks are vital in combating GBV. Nigeria’s Violence Against Persons Prohibition (VAPP) Act is a step in the right direction, but effective implementation and enforcement are critical. Policies must be backed by adequate resources and political will to ensure survivors receive justice and perpetrators are held accountable.
Conclusion
GBV is a multifaceted issue that demands a comprehensive response. Recognizing it as a health imperative underscores the urgency of coordinated action across sectors. Community leaders, educators, and religious institutions must be involved in challenging harmful gender norms and promoting respectful relationships. Educational programs that focus on gender equality and non-violent conflict resolution can foster a culture of respect and safety.
By prioritizing survivor-centred care, engaging communities, and strengthening legal systems, we can move towards a society where women and girls live free from violence and discrimination.
Speak Wednesday is an initiative of CFHI to address issues around gender-based violence and gender bias.
#SpeakWednesday #GBV #GenderBasedViolence #EndGBV #ViolenceAgainstWomen #DomesticViolence #EqualityForAll #GenderEquality #GenderBias
References:
- World Health Organization. “Violence against women.” WHO
- World Health Organization. “Gender-based violence is a public health issue.” WHO
- World Health Organization. “Strengthening health sector response to violence against women.” WHO
- International IDEA. “Funding and Oversight for VAPP Implementation.” International IDEA

SPEAK WEDNESDAY ON ADDRESSING GENDER-BASED VIOLENCE: A HEALTH IMPERATIVE Read More »